The structure and working principle of electromagnetic speed regulating motor
Structure and working principle of electromagnetic speed regulation asynchronous motor
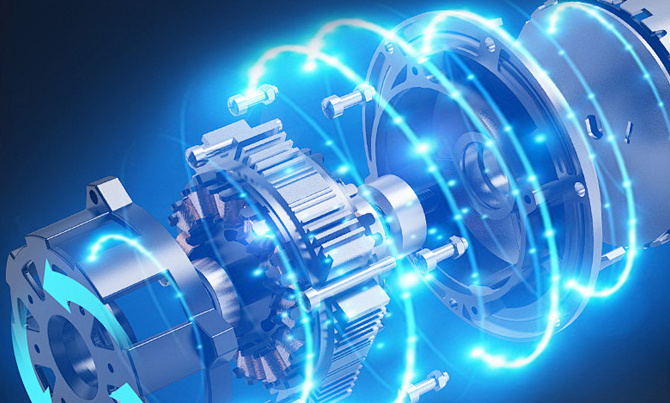
The electromagnetic speed regulation asynchronous motor is composed of three parts: ordinary squirrel-cage asynchronous motor, electromagnetic slip clutch and electrical control device. The asynchronous motor is used as the prime mover. When it rotates, it drives the armature of the clutch to rotate together. The electrical control device is a device that provides the excitation current of the excitation coil of the slip clutch. This paper mainly introduces the electromagnetic slip clutch, which includes three parts: armature, magnetic pole and excitation coil. The armature is a cylindrical structure made of cast steel, which is connected with the rotating shaft of a squirrel-cage asynchronous motor, commonly known as the active part; the magnetic pole is made of a claw-shaped structure and is installed on the load shaft, commonly known as the driven part. There is no mechanical connection between the active part and the driven part. When the excitation coil through the current generated magnetic field, claw structure will form many pairs of magnetic poles. At this time, if the armature is dragged to rotate by the squirrel-cage asynchronous motor, then it will cut the magnetic field interaction and generate torque, so the magnetic poles of the driven part will rotate with the active part of the armature, and the speed of the former is lower than the latter. Because only when the armature and the magnetic field have relative movement, the armature can cut the magnetic lines of force. The poles rotate with the armature. There is no essential difference between the principle and the principle that the rotor of an ordinary asynchronous motor moves with the rotating magnetic field of the stator winding. The difference is that the rotating magnetic field of the asynchronous motor is generated by the three-phase alternating current in the stator winding, and the magnetic field of the electromagnetic slip clutch is generated by the excitation coil. The DC current is generated, and the rotating magnetic field is played by the rotation of the armature.